
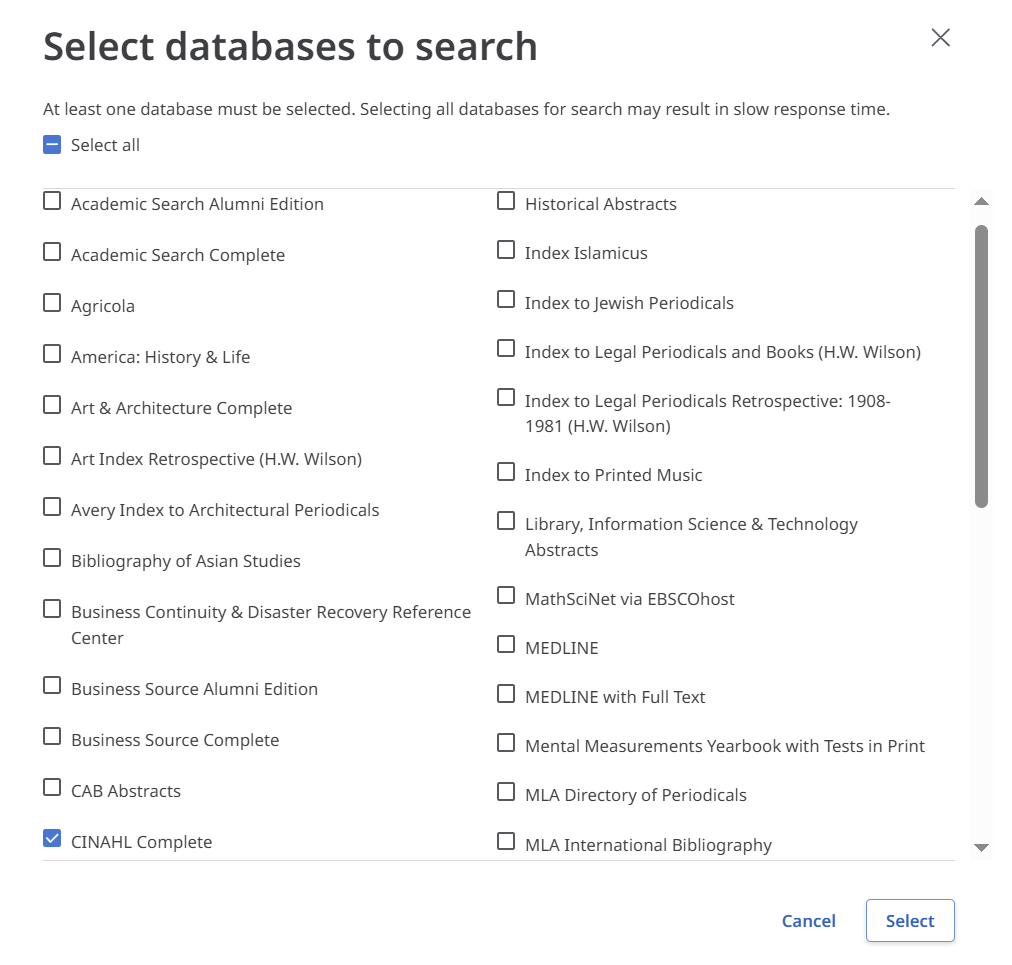
EBSCO is a platform that hosts databases across a range of disciplines. Key databases for health and medicine are:
 EBSCO Databases
EBSCO DatabasesSee EBSCO databases in other discipline areas.
All EBSCO databases have the same layout.
Click the  buttons below for more information.
buttons below for more information.

EBSCO has options for quick searches or comprehensive line-by-line searches
It helps to understand how databases work to construct a successful search strategy.
A keyword search:
looks for exact words in the database record
does not look in the full text.
Full-text search is possible in some databases, however not all items are covered.
A google search:
corrects your spelling
interprets your search (tries to guess what you want)
This means you need to think carefully about your words:
1. Meanings
2. Spelling
fetus VS foetus
![]()
3. Terminology
physiotherapy (Australia)
physical therapy (US)
![]()
If you have a simple search you can type the keywords in the search box.
EBSCO will search for each word within 5 words of each other.
You are able to use search connectors (AND, OR) and search techniques (truncation, proximity) in the basic search but it may be easier to go the guided form in Advanced search
For guidance on using the search connectors AND, OR as well as the techniques of truncation and proximity, see Search techniques below
We recommend line-by-line searching for systematic reviews, or other reviews where you need to search comprehensively. This is often required for publication.
Searching line-by line may be useful for a complex search as it gives you the power to check the impact of each search term and modify or troubleshoot individual terms.
Watch this video (4 minutes) on how to do line-by-line searching in EBSCO.
EBSCO has the option of different search modes
A filter refines your search. It checks your chosen criteria in each result, for example
and excludes results which don't meet the criteria.
Filters can be applied before or after your search
Before you search:
After you search:
You have personal account created automatically in EBSCO.
We recommend saving searches for assessments and major projects to ensure you don't have to re-type.
|
AND |
phototherapy AND aged | join concepts together with AND All of these terms must be included in each result |
|
OR |
(elderly OR aged) | join similar search terms together with OR Any of these terms can be included in each results |
|
phrase |
"pressure ulcer" | put search terms together in quote marks Words in in exact order included in results |
|
truncation |
genetic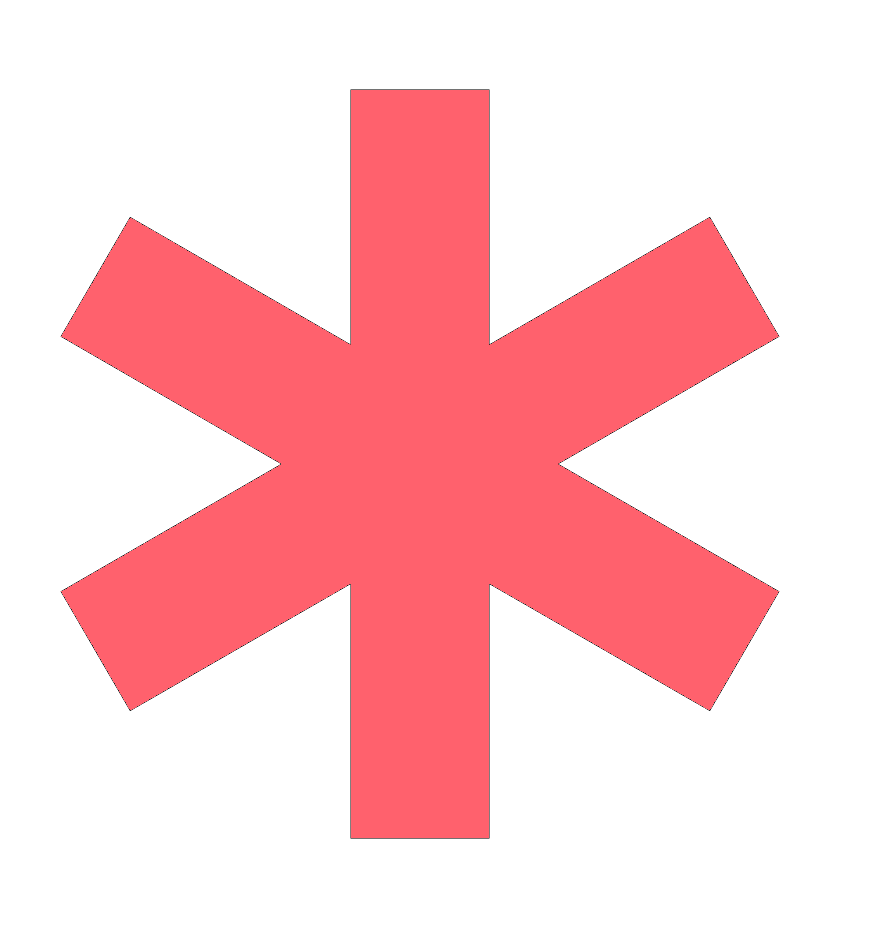 |
use the asterisk to retrieve variations on a word genetic* = genetic, genetics, genetically
|
|
proximity |
"middle ear" N2 infection |
words within a specific number "middle ear" N2 infection* = infections in the middle ear, middle ear infections |
Searches for variation of word endings.
![]() TRUNCATION
TRUNCATION
same word,
different ending
pressure ulcer* =
pressure ulcer
pressure ulcers
pressure ulceration
Instructions:
Useful for:
Example:
 Think carefully about possible words you are searching for, this is a common cause of irrelevant results.
Think carefully about possible words you are searching for, this is a common cause of irrelevant results.
pandemic* = pandemic, pandemics
pandem* = pandemic, pandemics, pandemonium
pande* = pandemic, pandemics, pandemonium, pander, pandering
Checks how closely search terms appear from each other..
![]() PROXIMITY
PROXIMITY
words within a
specific number
"middle ear" N2 infection
=
infection in the middle ear
middle ear infection
Instructions:
Use N or W and number of words you would like in-between the 2 search terms.
Near Operator (N)
| N1 | Next to each other, in any order, up to 1 word in between |
| N2 | Next to each other, in any order, up to 2 word in between |
Within Operator (W)
| W1 | Next to each other, in order they are entered, up to 1 word in between |
| W2 | Next to each other, in order they are entered, up to 2 word in between |
Useful for:
Example:


If proximity searching is back irrelevant results, you can
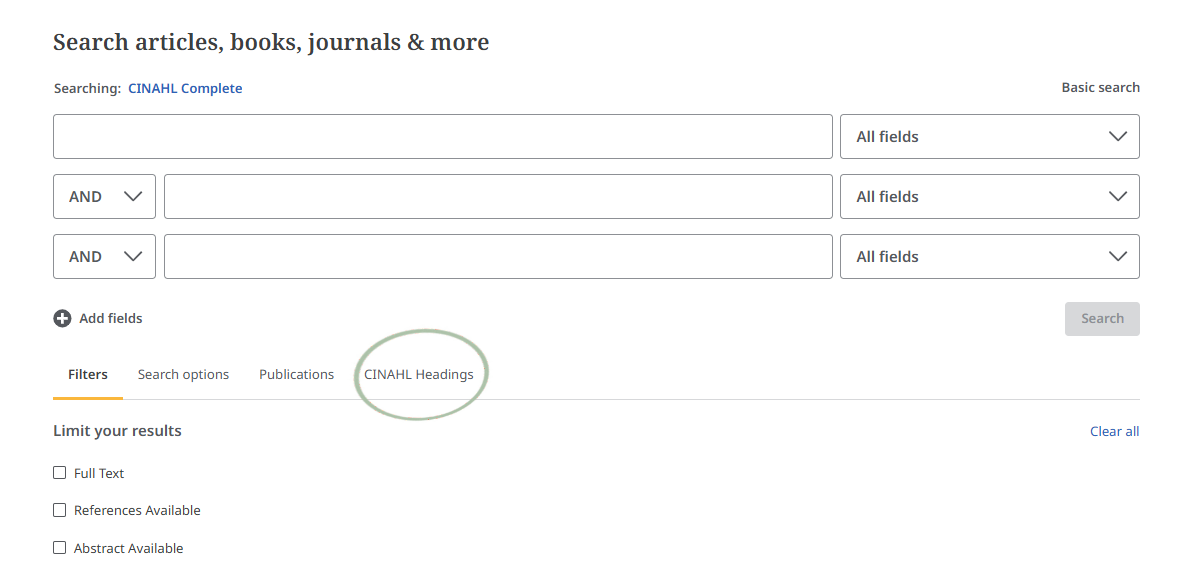
Watch this video (4 minutes) on the basics of subject headings (not specific to EBSCO).
Watch this video (4 minutes) on how to add a subject heading to a CINAHL search.
The steps are the same in other databases.
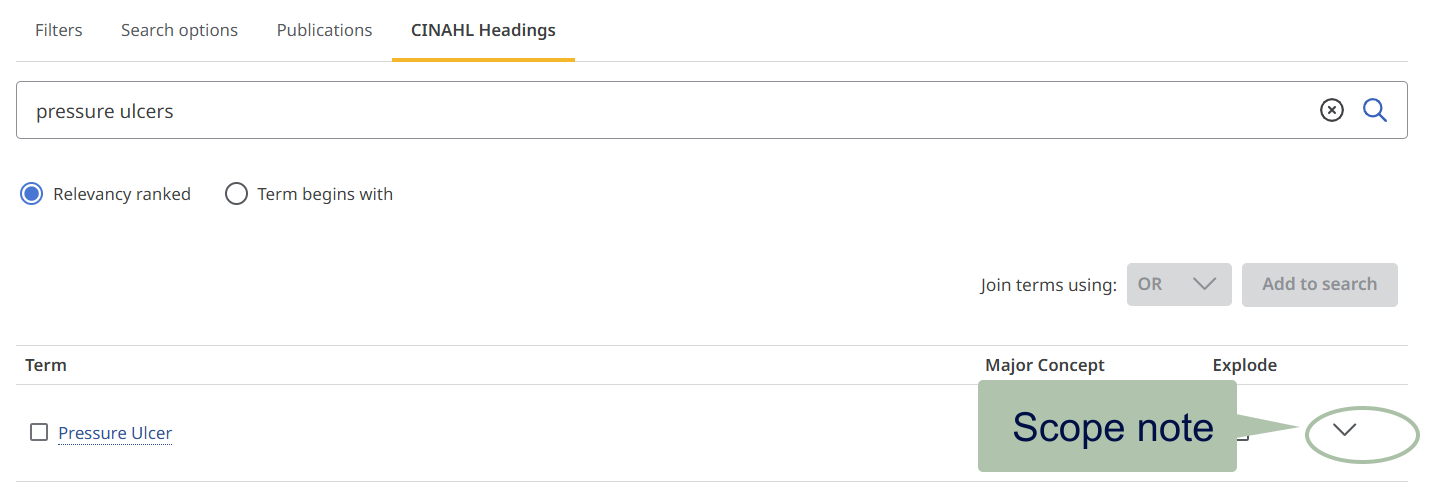
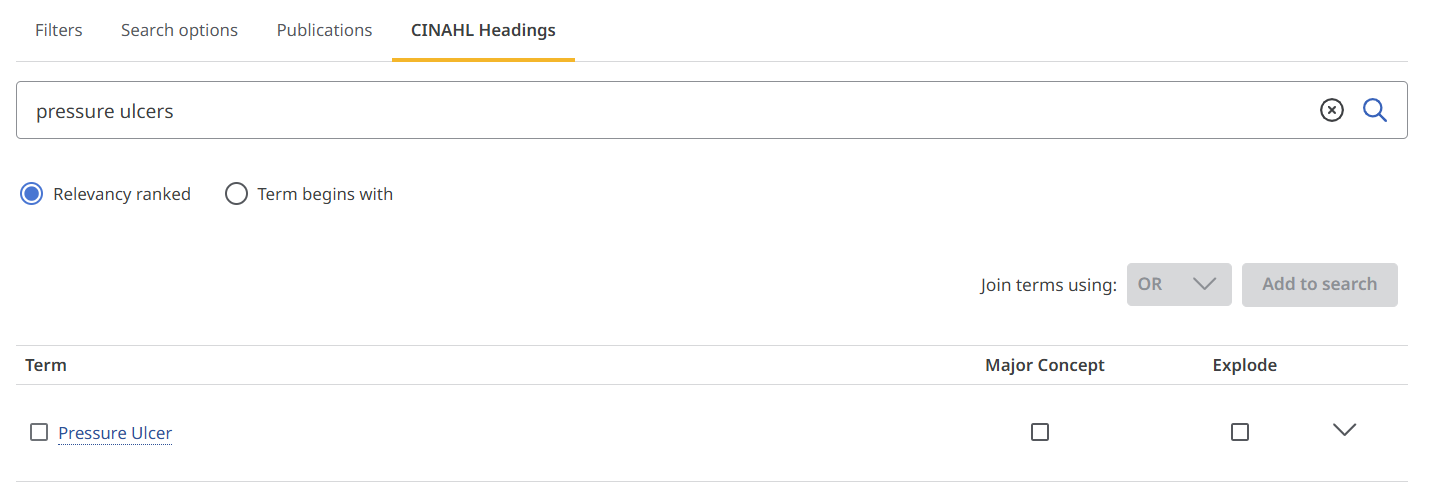
This will take you to the tree, showing where your heading sits in the hierarchy.
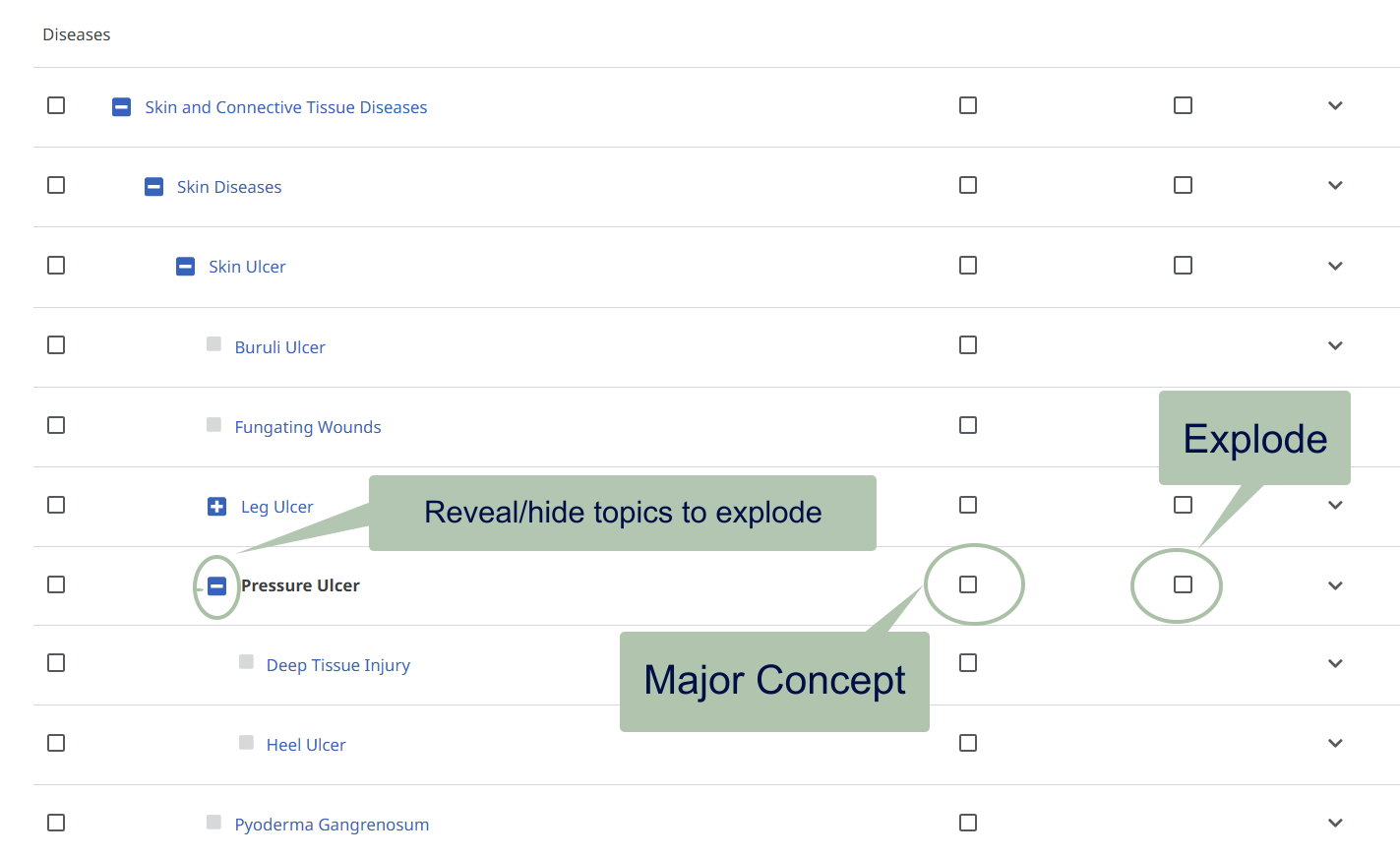
Subheadings describe an aspect of the main heading to narrow the focus.
More on subheadings.
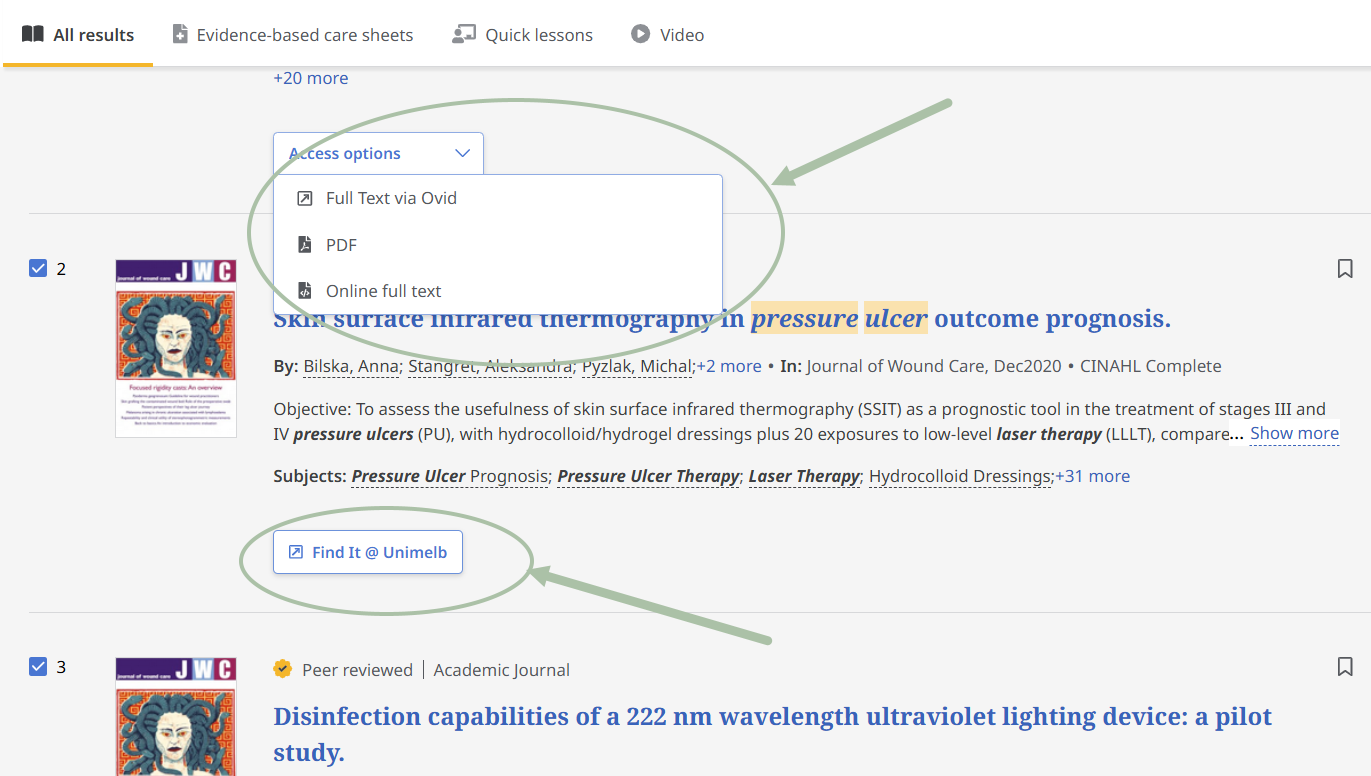
If you are having trouble accessing full text using instructions above try the following.
Canvas modules are available on the LMS, you just need to enrol using the links below. They feature instructions and activities to build your skills.
Curated information from University of Melbourne librarians. No login required.
Health Sciences & Medicine: